RAP or CAP: Which should your company follow?
- Sergio Cannelli

- May 24, 2025
- 6 min read

When choosing between RAP (Restful Application Programming) and CAP (Cloud Application Programming), it is crucial to evaluate which model best aligns with your environment and business objectives. RAP is designed for SAP-centric environments, offering a streamlined development process with Core Data Services (CDS), enhanced ABAP, business objects (BO) and business services, all integrated within Eclipse-based ABAP development tools (ADT). This makes RAP ideal for enterprises deeply integrated with SAP, particularly those using SAP S/4HANA. On the other hand, CAP is designed to create enterprise-grade cloud-native applications and services, leveraging languages, libraries and tools to support domain-driven design. CAP integrates well with open source and SAP technologies, making it an excellent choice for enterprises seeking flexibility, scalability and rapid development in a diverse technology landscape. Understanding these models will help you determine the right approach for your business.
What is ABAP Restful (RAP) development?
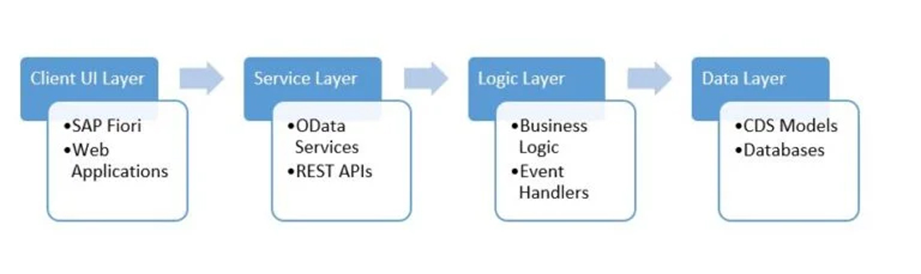
The ABAP RESTful Application Programming Model (RAP) provides a comprehensive framework for the optimised, end-to-end development of SAP HANA-optimised OData services crucial for Fiori applications. In addition, RAP facilitates the creation of various Fiori applications and the publication of web APIs, using various key technologies and frameworks.
RAP provides a standardised development workflow that integrates Core Data Services (CDS), an enhanced ABAP language, business objects (BO), business services and Eclipse-based ABAP development tools (ADT). This framework ensures efficient and consistent development processes.
The following image summarises these key elements:

Core Data Services (CDS):
Functionality: CDS enables the definition and consumption of complete data models within the SAP ecosystem. It provides a high-level declarative approach to creating semantic data models optimised for performance and consistency.
Benefits: Simplifies data modelling and ensures consistency across applications by allowing developers to clearly define data structures and relationships.
Infrastructure of the service model:
Functionality: This component is responsible for creating OData services, which are crucial for building Fiori applications and exposing APIs.
Benefits: Allows the linking of CDS views to OData services, which facilitates the creation and management of these services without the need for extensive coding.
ABAP-based application services :
Functionality: These services allow the implementation of customised business logic using ABAP, SAP's core programming language.
Benefits: Provides the flexibility to develop complex business processes and rules, ensuring that applications meet specific business needs and leveraging SAP's robust back-end capabilities.
SAPUI5-based user interfaces:
Functionality: SAPUI5 is a UI development toolkit for HTML5 used to create cross-platform and responsive web applications.
Benefits: Seamlessly integrates with backend services, providing a cohesive development experience and ensuring that the user interface is tightly coupled with the underlying business logic.
Key features and benefits
End-to-end development: RAP supports the entire development lifecycle, from defining data models and business logic to creating user interfaces and exposing APIs, ensuring that all components work together seamlessly.
Optimised for SAP HANA: Leverages the in-memory computing capabilities of SAP HANA to ensure high performance and efficient handling of large volumes of data.
Fiori application support: ideal for developing SAP Fiori applications, which provide a consistent, role-based user experience across devices.
Efficient API publishing: Facilitates easy API publishing via OData services, enabling consumption by a variety of clients, such as mobile applications, web applications and other enterprise systems.
Improved developer productivity: provides a unified framework with high-level abstractions, allowing developers to focus on business logic and functionality rather than low-level implementation details.
Future-proof architecture: designed to support future SAP technologies and innovations, ensuring the longevity and relevance of applications built today.
RAP is the preferred model for ABAP cloud and S/4HANA environments. Its main strength lies in its extensive ABAP CDS layer, which outperforms the CAP CDS layer. The ABAP programming language makes efficient use of native database capabilities, managing data at the database level wherever possible. This method, known as "run-time code pushdown", maximises database performance while maintaining the benefits of the ABAP language.
In addition, RAP introduces the concept of custom entities, which treats external APIs as CDS content. It is also planned to offer RAP services as function modules RFC, together with OData and REST. This ensures backwards compatible integration with traditional SAP Business Suite applications, such as ECC, without adding complexity.
What is Cloud Application Programming (CAP)?
The Cloud Application Programming (CAP) model is a comprehensive framework with languages, libraries and tools for building enterprise-grade applications and services. It also provides a structured reference path with best practices and out-of-the-box solutions.
Main features of the CAP
Domain-centred approach to development
Main objective: CAP prioritises domain-specific development, allowing developers to focus on business logic and domain models rather than getting bogged down in technical complexities.
Accelerated development : by emphasising domain-driven design, CAP accelerates the development process and ensures that applications are robust and aligned with business needs.
Ready-to-use solutions
Efficiency: CAP offers a wide range of out-of-the-box solutions for recurring tasks, helping developers avoid reinventing the wheel. This includes pre-defined modules and components that address common requirements.
Best practices: the framework guides developers through best practices, ensuring that implemented solutions are efficient, secure and maintainable.
Integration with open source technologies and SAP
Diverse technology stack: CAP integrates a combination of established open source and SAP proprietary technologies. This combination ensures that developers have access to a versatile and powerful toolset.
Broad adoption: the use of widely adopted technologies ensures compatibility and support, making it easier for developers to find resources and community support.
Benefits of the CAP
Investment protection:
Future-proof: CAP is designed to protect investments by enabling applications to adapt to evolving cloud technologies. This ensures that applications remain relevant and functional as the technology landscape evolves.
Scalability: The framework supports scalable solutions, making it suitable for growing businesses and increasing data demands.
Improved developer productivity:
Simplified development: By offering out-of-the-box solutions and following best practices, CAP simplifies the development process. Developers can focus on creating features that add value to the business instead of dealing with basic technical details.
Consistency: Structured approach and standardised practices lead to more consistent and reliable applications.
Ecosystem rich:
Comprehensive tools: CAP includes a wide range of tools that assist in various aspects of application development, from coding and testing to deployment and maintenance.
Community and support: The framework benefits from a strong community and extensive documentation, which offers support and resources to developers.
What differentiates the CAP from the RAP?
Concluding the above in-depth explanations of the two development approaches, let us now look at the key differences between them.
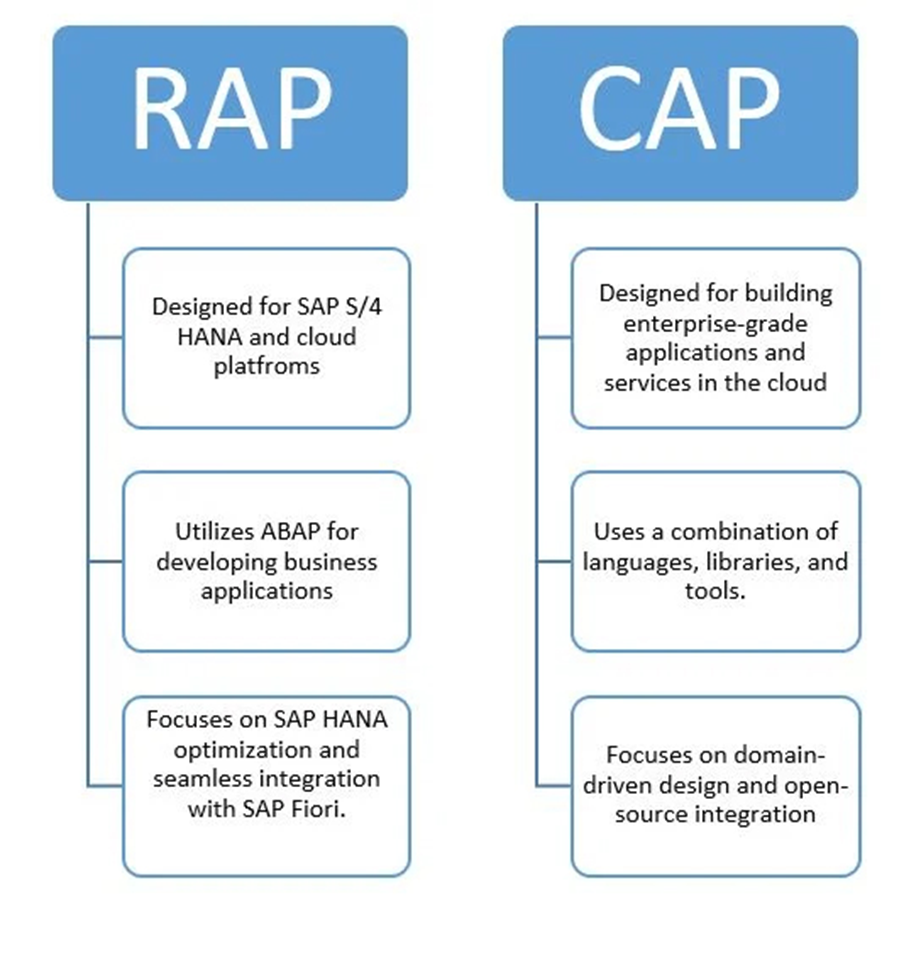
RAP is ideal for developing applications in SAP S/4HANA and SAP Cloud Platform environments, especially for projects that require deep integration with SAP Fiori and ABAP. On the other hand, CAP is ideal for developing cloud-native applications and services, making it ideal for projects that require flexibility in the technology stack and integration with various cloud providers.
Therefore, choosing between RAP and CAP involves understanding the specific needs of your organisation, your current infrastructure and your future goals. If your environment is heavily SAP-centric and requires deep integration with SAP systems, RAP offers robust performance and seamless integration with the SAP ecosystem. However, if you are looking for a more flexible, cloud-native approach that integrates with a variety of technologies and platforms, CAP offers a versatile solution that supports multiple programming languages, databases and rapid development.
By carefully evaluating these factors, you can make an informed decision that aligns with your strategic objectives and technical requirements.
Parameter | SAP CAP | SAP RAP |
Primary Usage | Develop cloud-native applications and extensions | Develop and expose APIs as OData services in a RESTful manner |
Development Environment | Cloud environments like SAP Business Technology Platform | Primarily in SAP S/4HANA systems (on-prem or cloud) |
Programming Language | Primarily uses Node.js, and Java | ABAP |
Architecture Style | Microservices architecture Monolithic architecture | Monolithic (though supports decoupling) |
Data Modeling | CDS Views, using SQL-like syntax | ABAP CDS Views, using ABAP language |
Service Exposure | OData V4 | OData V2 and V4 |
Main Benefits | - Agile and rapid development | - Deep integration with existing ABAP stack |
- Scalability and flexibility | - Robust and stable, with mature ABAP features | |
- Cloud-native features and microservices support | - Utilization of existing ABAP skill sets | |
- Supports various DBs and environments | ||
- Might require restructuring for existing solutions | - Might require additional training in RESTful concepts | |
Ideal Use-Cases | - Cloud-native application development | - Exposing business services/APIs from S/4HANA |
- Multi-cloud and hybrid cloud scenarios | - Leveraging ABAP business logic | |
- Agile and scalable solutions | - When dealing with complex, transactional logic | |
Integration Aspects | - Better suited for integration with cloud solutions | - Direct and deeper integration with SAP S/4HANA systems |
Deployment | Cloud deployment, suitable for SaaS models | On-prem and cloud (within S/4HANA) |





Comments